The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965: Employee Eligibility, Rules & Calculation

Table of Contents
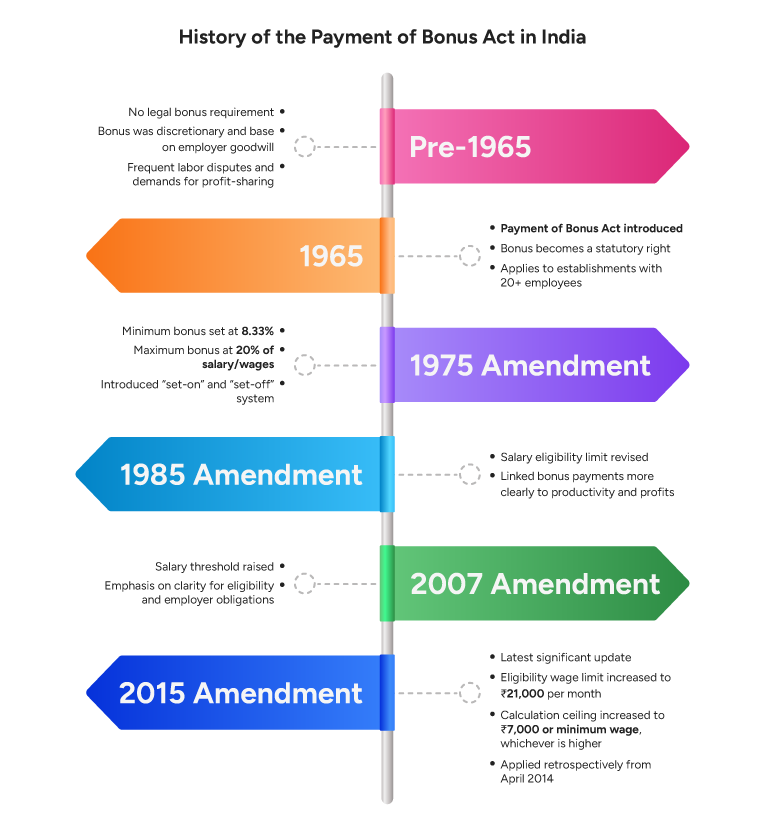
The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965, also known as the Bonus Act, is an Indian law that mandates the payment of bonuses to employees. The Act applies to certain establishments that meet specific criteria. A company distributes bonuses to its employees based on profits and productivity. The Payment of Bonus Act provides for a minimum bonus of 8.33% and a maximum bonus of 20% of an employee’s salary. Additionally, employers are required to pay the bonus in cash within eight months of the closing of the accounting year. The government enforces the Bonus Act with the Payment of Bonus Rules 1975, and amends the act from time to time to keep up with the cost of living.
The Payment of Bonus Act Updates in November 2025
- The government issued a notification repealing the Payment of Bonus Act and replacing it with the new Code on Wages, effective from November 21, 2025.
- The Code on Wages, 2019, will replace the old wage and labour laws and consolidate them into four labour codes.
- The last major change before this was in 2015, when the government amended the Bonus Act and increased the bonus limit to ₹7,000.

What is the Payment of Bonus Act?
The Payment of Bonus Act, 1965, is one of India’s wage and labour laws that mandates minimum and maximum bonuses for employees. The act was enacted in 1965 and has since been amended to account for changes in cost-of-living factors. The Indian parliament passed the act to address the growing number of industrial disputes between employers and employees, thereby bringing uniformity to the bonus structure. The government operationalized the act by passing the Payment of Bonus Rules 1975.
The Payment of Bonus Rules, 1975
These rules were passed under section 38 of the Payment of Bonus Act 1965. There are mainly three important rules, namely –
- Rule 3: Authorizes the central labour commissioner and state labour commissioners to grant permissions for the change of accounting year.
- Rule 4: Makes it mandatory for employers to maintain registers related to computation, allocation, payroll deductions, and bonuses given to each employee.
- Rule 5: Makes it mandatory for employers to send the annual returns to the appointed inspector.
The Payment of Bonus Act Applicability
Sections 1 and 3 of The Payment of Bonus Act detail the applicability criteria, while Section 32 lists exemptions. First, we will see the sectors/establishments covered under sections 1 and 3. Then, we will list the exemption criteria provided under section 32 of the Bonus Act. This helps employers clearly understand who is eligible for bonus payouts and who is not.
Where does the Bonus Act Apply?
The bonus act in India applies to –
- Every factory and establishment with 20 or more employees.
- Any establishment that employs 10 or more employees may also need to pay a bonus if the government notifies it.
- Every department and branch of an establishment, whether located in the same place or a different place, is also covered under the Payment of Bonus Act.
Which Institutions are Exempted under the Payment of Bonus Act?
The exempted institutions include:
- The Life Insurance Corporation of India,
- Other insurance agencies,
- Industries under the authority of the central/state government, or a local authority (municipalities and more),
- The Indian Red Cross Society and similar non-profit organizations,
- Educational institutions, including universities,
- Any state/central financial institution constituted under the Deposit Insurance Corporation Act, 1961, with a capital of more than one crore rupees,
- Employees employed in any public sector institution.

Who is Eligible, and Who is Exempt from Receiving Bonus under the Bonus Act in India?
Sections 8, 9, 12, 13, 17, 18, 19, 20, and 32 define the eligibility criteria in the Payment of Bonus Act:
- Section 8: An employee must have worked for at least 30 days in any establishment for the accounting year, and
- Section 3: All the employees of an establishment with more than 20 employees and of any department or branch of such an establishment.
Employees who are exempt from the bonus act include:
- Section 9: An employee is disqualified from receiving a bonus in that accounting year if they are engaged in theft, violent behaviour, misappropriation, or sabotage of property.
- Section 32: As mentioned, employees employed in certain institutions, such as non-profit, central/state financial institutions (other than banks), and public sector industries, are exempt.
- Seamen as defined in the Merchant Shipping Act, 1958.
| Bonus Act Timeline & Penalty Table | ||
|---|---|---|
| Requirement / Event | Timeline / Deadline | Penalty for Non-Compliance |
| Calculation of bonus for the financial year | After closing of accounts and determination of allocable surplus | Delay may trigger interest payments or legal claims |
| Mandatory payment of bonus | Within 8 months from the end of the accounting year (can be extended by government approval) | Fine up to ₹1,000 or 6 months’ imprisonment, or both |
| Filing annual bonus return if applicable | Within the prescribed period after bonus distribution | Fine for failure to maintain or produce records |
| Maintaining bonus-related records | Continuously throughout the year | Penalties for improper or missing documentation under the Act |
| Payment of minimum bonus | Even if company has no allocable surplus, subject to certain conditions | Legal liability for violation and possible employer prosecution |
| Payment of bonus to eligible employees | Employees who worked at least 30 working days | Employee can legally claim non-paid bonus through authorities |
| Recovery of unpaid bonus | Employee may apply to authorities within one year from due date | Company can be ordered to pay pending bonus + delay interest |

How to Calculate Bonus in India According to the Bonus Act?
Here is a step-by-step guide that can help you calculate bonuses in India. We will cover the calculation process and the set-on and set-off concept. Then, we conclude with a real-life example.
Calculation Steps
- Check whether the employee is eligible under the Act, meaning their monthly wages do not exceed ₹21,000 and they have worked at least 30 days in the accounting year.
- Determine the salary to be used for calculation, capped at ₹7,000 or the applicable minimum wage, whichever is higher.
- Calculate the annual salary by multiplying the monthly salary by twelve.
- Apply the minimum bonus rate of 8.33 percent on the annual salary calculation.
- Apply the maximum bonus rate of 20 percent only if the allocable surplus permits.
- Adjust the amount using the set-on or set-off provisions, if they apply, during that accounting year.
- Ensure the bonus is paid within eight months from the end of that financial year.
Set-On and Set-Off Bonus Calculation
- Set-on occurs when the allocable surplus is higher than the amount required to pay the maximum bonus for that year.
- The excess surplus is carried forward for up to four accounting years and can be used to support bonus payments in low-profit years.
- Set-off occurs when the allocable surplus is not sufficient to pay the statutory minimum bonus.
- This shortfall can be carried forward for up to four years and adjusted against future surpluses.
The bonus calculation, with a real-life example, is described below.
Scenario: An eligible employee earns ₹14,000 per month. The minimum wage applicable to the role is ₹12,500.
- Calculation salary = higher of ₹7,000 or ₹12,500 → ₹12,500.
- Annual calculation salary = ₹12,500 × 12 → ₹150,000.
- Minimum bonus = 8.33 percent of ₹150,000 → ₹12,495.
- If the employer declares a 10 percent bonus:
10 percent of ₹150,000 → ₹15,000. - If the employer declares a 20 percent bonus:
20 percent of ₹150,000 → ₹30,000.
Set-on example: If the surplus allows a 25 percent bonus, only 20 percent can be paid. The surplus, equal to the additional 5 percent, is set aside and carried forward.
Set-off example: If surplus supports only a 4 percent bonus, the employer still pays 8.33 percent. The deficit is set off and carried forward to future years.
Minimum Bonus and Maximum Bonus
The minimum bonus is the statutory floor (8.33% of an employee’s basic salary, or the prescribed minimum amount) and applies even when the surplus is limited. The maximum bonus is capped at 20% of an employee’s basic salary and is payable only when the allocable surplus is sufficient.
| Growth of Bonus Eligibility & Range Under the Bonus Act | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Eligibility Salary Limit | Bonus Range |
| 1965 | ₹750 | 8.33–20% |
| 1995 | ₹3,500 | 8.33–20% |
| 2007 | ₹10,000 | 8.33–20% |
| 2015 | ₹21,000 | 8.33–20% |
The Payment of Bonus Act: A Quick Recap
The Payment of Bonus Act is a statutory measure that ensures that employees receive sufficient bonus from the employer’s profits. The act defines applicability criteria, provides for the calculation of bonuses, lists exemptions, and sets out a set of provisions. The payment of bonus rules also specify the state/central labour commissioners as authorities that grant permissions for the start of any accounting year for any establishment. Lastly, in November 2025, the government issued a notification that merges the provisions of the Payment of Bonus Act with the Code on Wages, 2019.

FAQs
Does the Bonus Count as Part of CTC, or is It Separate?
The bonus of the Payment Act does not regulate the CTC structure, so employers may include a statutory bonus within CTC or keep it separate.
What are an Employer’s Responsibilities under the Bonus Act?
Employers must determine applicability, correctly compute eligibility and calculate wages, calculate available and allocable surplus, apply set-on/set-off where relevant, pay statutory bonus on time, and maintain prescribed records.
What is the Meaning of Allocable Surplus in the Bonus Act?
Allocable surplus is the portion of an establishment’s available surplus designated for bonus distribution after permitted deductions; it governs whether employers can pay above the statutory minimum bonus.
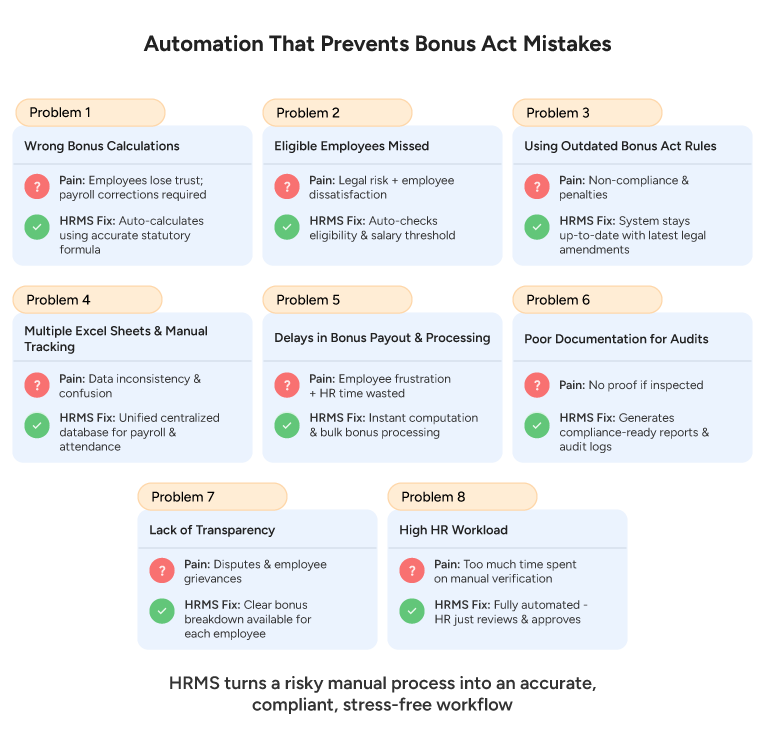
What Issues Commonly Arise for Employers when Calculating Bonus Eligibility?
Common problems include mixing up the eligibility ceiling versus calculation ceiling, using gross instead of permitted salary components, incorrect surplus computation or tax adjustments, and misapplying set-on/set-off carryforwards.
How Can HR Ensure Bonus Act Compliance?
HR can ensure Bonus Act compliance by:
- Maintaining proper employee records and wage data
- Calculating bonus accurately as per eligibility rules
- Paying bonuses within the statutory timeline
- Keeping updated with amendments to the Act
- Using reliable payroll tool to avoid calculation errors
- Documenting bonus payments for audit and legal verification
What Bonus Rights do Employees have?
Eligible employees have a statutory right to at least the minimum bonus and, where allocable surplus permits, to a proportionate bonus up to the statutory maximum bonus. They also have the right to timely payment and to challenge non-payment through the prescribed authority.
What Bonus Rights do Employers have?
Employers can disqualify an employee from receiving a bonus for misconduct, theft, misappropriation, and violent behaviour on the premises. They can also deduct bonuses if an employee has worked for less than 30 days.
What Offences Can Disqualify an Employee from Receiving the Bonus?
Specified misconduct, such as fraud, riotous or violent behavior connected with employment, theft, misappropriation, or deliberate damage to employer property, is grounds for disqualification for that accounting year.
Grow your business with factoHR today
Focus on the significant decision-making tasks, transfer all your common repetitive HR tasks to factoHR and see the things falling into their place.

© 2026 Copyright factoHR


