Payroll Components: The Complete Guide for 2026

Table of Contents
With today’s fast-paced environment, maintaining accurate payroll records is not only a matter of routine HR but also a legal and ethical requirement. It has been found that over 50% of workers think about leaving their job when payroll-related errors occur repeatedly. This shows the key role of proper payroll administration in following regulations and employee satisfaction.
As organizations navigate through 2025, payroll automation and evolving compliance requirements define business operations. Understanding payroll components is more critical than ever. This detailed guide will take you through every aspect of payroll—from core components to modern trends—to help streamline processes, avoid penalties, and maintain trust with the workforce.

What are Payroll Components?
Payroll components are the various elements that make up an employee’s total compensation. These elements help calculate employees’ net salary and deductions. These components show both the gross salary and net salary for each employee. Organizations can ensure fairness, transparency, and legal compliance through the use of payslips. Some of these components are:
- Basic salary
- Allowances
- Bonuses
- Commissions
- Paid Time-off
- Expense reimbursements
- Contributions to provident funds
Getting them right means paying employees accurately and on time, while also meeting statutory regulations.
What are the Core Components of Payroll?
Here are the basic elements of payroll that any organization needs to know to handle payroll effectively.
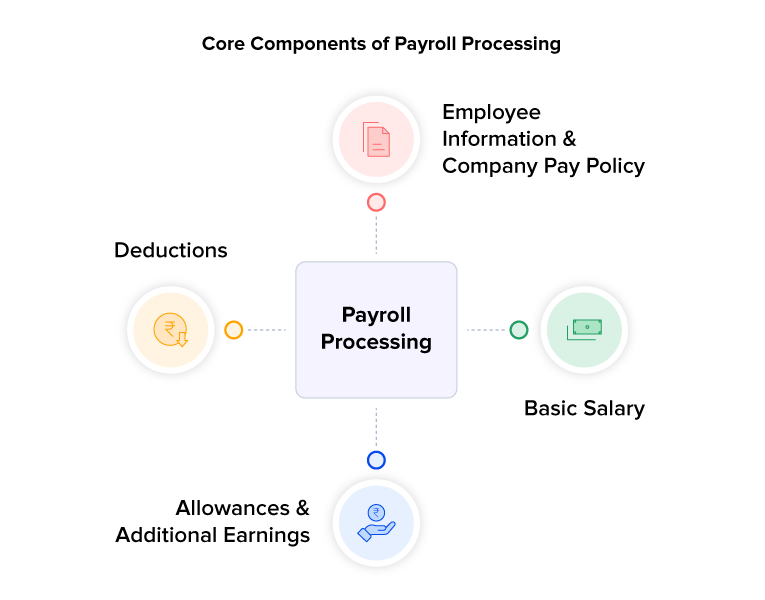
A. Employee Information & Company Pay Policy
The foundation of payroll starts with accurate employee data and well-defined compensation policies. Key information includes:
- Name and designation
- Joining date
- PAN, Aadhaar, and bank details
- Compensation structures
- Benefit administration
The pay structure (fixed, variable, or both) used in a company shapes the payroll system.
B. Basic Salary
This is one of the core components of salary. Typically, it accounts for 50-60% of the total salary. It’s fully taxable and used as a reference point for calculating other components, such as:
- Provident fund (PF)
- Gratuity
- Bonuses
The basic salary provides stability and forms the guaranteed income for your workforce.
C. Allowances & Additional Earnings
These are the variable elements added to the basic salary to support employees with work-related or personal expenses. Common types include:
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): Offered if the employee lives in rented accommodation in a different city.
- Dearness Allowance (DA): Compensates for inflation for government employees.
- Conveyance Allowance: Covers travel expenses from home to work.
- Medical Allowance: Helps with healthcare expenses.
- Special Allowance: A flexible component often used to balance CTC.
These allowances may be fully taxable or partially exempt, depending on applicable laws.
D. Deductions
Not everything in the payslip is about additions—some parts reduce the gross salary for compliance and financial obligations. Deductions are of two types:
1. Statutory Deductions (Mandatory)
- Provident Fund (PF): A retirement benefit; both employer and employee contribute 12% of basic salary, wherein 8.33% goes to the Employee Pension Scheme (EPS), and the remaining 3.67% goes to the Employee Provident Fund (EPF).
- Employee State Insurance (ESI): Applicable if gross salary is below ₹21,000 in India.
- Professional Tax (PT): Charged by some state governments.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): Tax deducted from an employee’s salary by the employer.
2. Voluntary Deductions
- Loan payments
- Voluntary provident fund contributions
- Insurance premiums
- Salary advances
These deductions affect the net salary and must be recorded carefully to avoid compliance risks.

What is the Difference Between Gross Salary and Net Salary?
Understanding the difference between Gross Salary vs Net Salary is essential for payroll transparency:
- Gross Salary = Basic Salary + Allowances + Bonuses (before deductions)
- Net Salary = Gross Salary – Deductions (what the employee takes home)
For example, if an employee’s gross salary is ₹60,000 and deductions total ₹10,000, their net salary will be ₹50,000.
Advanced Payroll Components in 2025
As businesses evolve, their payroll structures become increasingly complex. Here are some advanced components to consider:
1. Bonuses
Bonuses are performance-based incentives paid quarterly, annually, or project-wise. They are part of an employee’s overall earnings and require proper calculation and record-keeping to stay compliant.
2. TDS (Tax Deducted at Source)
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) acts as a direct taxation method where employers deduct a percentage of an employee’s salary as tax before disbursing it. Various components of salary that affect TDS calculations are:
- House Rent Allowance (HRA) is partially or fully exempted.
- Section 80C investments
- Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
- Other deductions declared by employees
TDS must be deposited monthly and accompanied by Form 16, which is issued yearly.
3. Employee Benefits
Benefits aren’t always part of the monthly salary but add significant value. These may include:
- Health and life insurance
- Retirement plans (NPS, Superannuation)
- Meal cards and transport benefits
- Work-from-home stipends (emerging trend post-pandemic)
Employee benefits play a role in boosting how employees feel about their work and sometimes help reduce the company’s tax burden.

Modern Payroll Trends and Best Practices (2025)
To address evolving compliance and employee expectations, companies should adopt smarter payroll calculation practices.
1. Payroll Automation & Cloud-Based Systems
Manually performing payroll calculations is time-consuming and prone to errors. Cloud payroll software makes sure that:
- Real-time data access
- Automatic tax calculations
- Payslip generation
- Compliance updates
2. On-Demand Pay & Digital Compensation
Employees today want flexibility when it comes to compensation. On-demand pay, also known as earned wage access (EWA), refers to withdrawing a portion of earned wages before an employee’s scheduled payday. Digital wallets and UPI-based salary disbursals are becoming common in India and globally. It improves:
- Financial wellness
- Job satisfaction
- Employee retention
3. HRMS & Accounting Integration
It reduces the burden on HR professionals and finance teams, increasing transparency and efficiency. Integration of Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) and accounting software with payroll offers:
- Seamless data flow
- Accurate financial reporting
- Better workforce analytics
4. Regular Payroll Audits
Having multiple audits allows issues to be spotted more easily and prevents legal issues. Using the payroll tool can help automate payroll-related tasks and maintain accurate audit trails.

Conclusion
Understanding payroll components is important for both the company and its employees. Organizations should know that payroll components involve calculating salaries and other associated benefits. Employees should be aware of how their salary is calculated and what each part of their salary stands for. It helps maintain accuracy and ensures the company remains compliant. Transparent and timely payroll processes increase employee trust and morale.
A well-structured payroll system helps organizations stay compliant with labor laws and maintain employee satisfaction. Audit your current payroll process, implement automation, and stay updated on legal changes for 2025. Payroll audit made easy with factoHR. Schedule a demo now to know more!
FAQs
What are the Components of the Payroll System?
Usually, a payroll system covers the following:
- Employee data management
- Salary structure configuration
- Attendance & leave integration
- Tax and statutory compliance
- Payslip generation and reporting
- Payment disbursement
- Documentation and reporting
What are the Five Payroll Steps?
- Gather employee information and monitor attendance
- Calculate gross salary
- Apply deductions
- Verify and generate payslips.
- Transfer salary and file compliance reports
How does Payroll Compliance Work?
Payroll compliance involves adhering to government laws around tax, PF, ESI, and professional tax. Timely deductions, filings, and accurate records are necessary to stay compliant and avoid penalties. If an organization fails to comply, it can face legal actions and audits.
What are Statutory vs. Voluntary Deductions?
- Statutory deductions are legally mandated (e.g., PF, ESI, TDS).
- Voluntary deductions are opted in by the employee (e.g., insurance, loans).
Grow your business with factoHR today
Focus on the significant decision-making tasks, transfer all your common repetitive HR tasks to factoHR and see the things falling into their place.

© 2026 Copyright factoHR


