Understanding Employment: Know More about the Benefits of Non-Exempt Employees
Table of Contents
With distinct job types like full-time vs part-time, exempt vs non-exempt, have you ever wondered why employees have these options?
What makes these job types different from each other?
What makes an employee choose between these types?
These job types help employees adjust according to their needs and family requirements. Some students wanted to compensate for the charges of their study. Others wanted to establish a balanced work-life. Some wanted to earn more while having total freedom in the office. These different attitudes of individuals have triggered the society to create such employment types that may be suitable according to their needs.
Apart from benefits, it is essential for the employer to understand the difference and liabilities of the employment types. Many of the employees choose non-exempt employees to receive a balanced work-life situation. Here’s the basic understanding of the Non-exempt Employee, the definition, the benefits and how it differs from the exempt employees.

What is a Non-Exempt Employee?
The non-exempted employees fall under an employment type that is protected under the labour laws by the central government. The employer can never change the regulations of the non-exemptions. Such employees are the ones who are entitled to the minimum pay, overtime pay, bonus, and other benefits from the government with a minimum of 35-40 hours of work. These overtime hours are the hours worked above the assigned working hours to the employee.
Moreover, the status of employment also depends on the type of responsibility the employees are assigned. They are typically assigned the lower posts exclusive of the managerial work.
Why is Understanding Non-exempt Employees Essential?
Though compared to exempted employees, non-exempt ones may be paid lesser, but still, as an employment category, it is important to understand it.
Being protected by the labour laws, the employer must take the utmost care in the salary calculation of the non-exempt employees. The Minimum Wages Act, 1948, helps employees receive at least the minimum wages, from their employer. Moreover, if the employees work above the specified hours, then they should be entitled to the exact overtime payment decided under the laws.
Despite using an automated payroll management software, the employer should compulsorily include all the calculations during salary processing. Even a small error in the same can bring some severe allegations to the company, thus degrading the status. Whereas that is not the case with exempted employees as neither their payroll is never fixed nor they are protected under the laws.

What are The Benefits for Non-Exempt Employees?
There must be some reason for creating more than one type of employment options for employees. Knowing the importance of non-exempt employees for employers is not enough. The employees also find benefits in choosing between non-exempt employment, and here are the reasons why.
1. Fixed Working Hours
Though it changes according to the employment type, Non-exempted employees only have to work for fixed hours. In these fixed hours, they are monitored thoroughly. They are not allowed to breach the laws of fixed hours and breaks. But apart from these regulations, an employer cannot ask them to work extra hours regardless of their own wish.
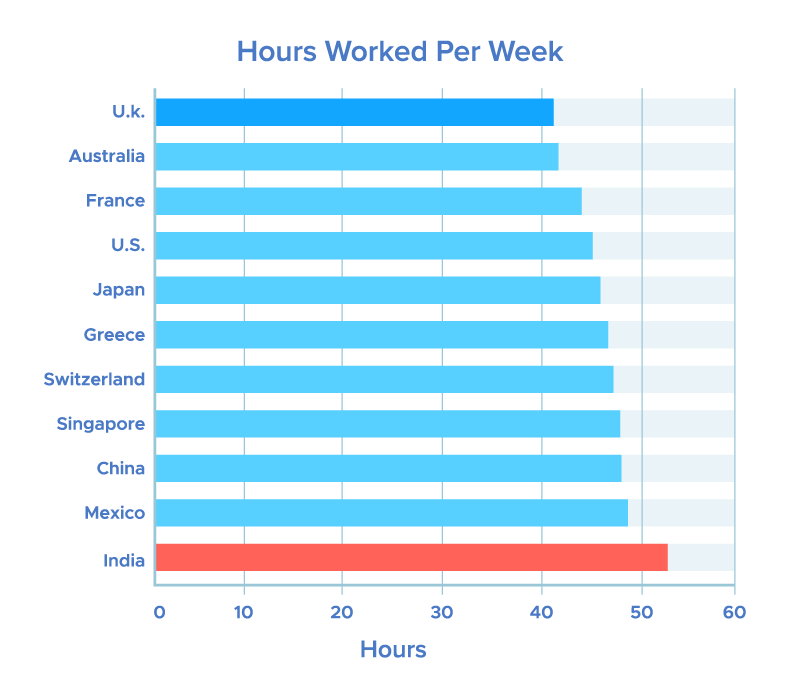
As shown in the image, Indian employees spend more hours on work as compared to other countries’ employees.
2. Minimum Pay
The employees under the non-exempted type regardless of their net pay must be paid the minimum salary as per the rules formed under the Minimum Wages Act, 1948. Despite their time and detailed, the employer is liable to pay them the exact minimum pay, calculated based on the actual working hours. The more you work, the more you earn.
However, exempted employees may receive more or less, but again they don’t have to come under any rules of the government.
3. Overtime Benefits
Perhaps the biggest advantage for the non-exempt employees is they can receive overtime compensation for their extra hours worked. Calculation of overtime can be pro-rata based. For example, If an employee has worked ‘x’ hours extra apart from the assigned hours, they must be compensated accordingly.
But on the contrary, the employer is not liable to pay the overtime compensation in case of exempt employees.
4. Rights and Rewards
Since non-exempt employees come under the laws of accurate payment and over time, they are also entitled to the bonus and yearly rewards that are necessary from the legislative point of view. Moreover, they can also protect their employee rights given to them.
5. Unemployment Insurance
Not to mention, but both exempt and non-exempt employees can receive unemployment benefits due to a cause exclusive of resignation or termination of employment. The employment can be lost due to permanent closure, disablement, or retrenchment. Under such conditions, the Rajiv Gandhi Shramik Kalyan Yojna protects them by offering insurance to the unemployed.
6. Work-Life Balance
As per the reports of the hindu business line, about 60% of the Indian millennials feel their work-life balance is near to ‘terrible’. And thus employees move towards the job, delivering less effect on personal life.
Though non-exempt employees are monitored regularly of their activities in the office, they are only asked to work till assigned hours. If they want to work above, it is up to them. But as they have only a fixed amount of hours to work and are never requested to work extra to complete the task, it is easy to establish a balance between work-life and personal life.

How do Non-exempt Employees Differ from Exempt Ones?
Though there are restrictions and a comparative lower salary than the exempt ones, people many times choose the non-exempt job because mostly they receive labour law security that others don’t. Employers cannot neglect or breach the terms of legislative laws for such employees. The employer has to consider perfect salary processing, benefits and other rights.
Moreover, like exempt employees, they are not pressurized to complete the tasks as soon as possible, but with the restriction on time punctuality and working hours completion.
Unlike exempt employees, the salary received by non-exempt employees is always according to the Minimum Wages Act. 1948. Though it can be greater than that but never lower. In contrast, the salary of exempt employees can go below minimum wage but also can rise higher based on work.
But as the exempt employees, regardless of their freedom of time, fulfil the task, the company has more expectations from them, and they can be more benefited from the company. For example, day-offs, unique recognitions, promotions, etc.

Ending Notes
As far as employment is considered, employees are free to choose the ones they are comfortable with. The employers need to understand the basic differences between them to bifurcate them equally. They need to consider all the liable benefits that an employee may receive. Because breaching such laws can levy fines which employers never want. Thus it is better to know what your employee’s employment type is.
For employees choosing non-exempt jobs, the company must ensure that they receive all the benefits and rights without any favouritism. Majorly they have a proper bifurcation of work and personal life, and thus this category is more choosable in the employee network.
Grow your business with factoHR today
Focus on the significant decision-making tasks, transfer all your common repetitive HR tasks to factoHR and see the things falling into their place.

© 2025 Copyright factoHR


