21 Key Functions of Human Resources Management (HRM)

Table of Contents
HRM functions are a set of core operations that the HR department performs to improve people management. These functions are essential for any organization, as they help align human resources with business objectives.
They are also important for managing employee lifecycles. Operational HRM functions improve administrative support. Functions like workplace safety and compliance with wage and labour laws help mitigate risks and ensure compliance with regulations.
This blog discusses the definition of core HRM functions and explores the managerial and operational functions of human resources. We conclude by examining the importance of these functions and answering some of your frequently asked questions related to the role of human resource management.
Key Takeaways
- The core functions of HRM include a set of key operations that combine both managerial and operational aspects of human resource management.
- Managerial functions include strategically important areas, including HR planning, talent management, organizational development, and change management.
- Operational HRM functions focus on core HRM activities related to the employee lifecycle, such as recruitment, onboarding, and employee relations. They also include compliance and risk mitigation.
- These functions are important for four reasons:
- Strategically, they align human resource planning with business objectives.
- They also streamline processes related to the employee lifecycle.
- HRM functions enhance risk mitigation and facilitate compliance with regional and global regulations.
- Operational HR functions improve support mechanisms that enhance employee relations and workplace safety.

What are the Functions of HRM?
The core functions of HRM include operations such as recruitment, onboarding, talent management, succession planning, and change management. These functions are divided into two categories: managerial HRM functions and operational HRM functions.
Managerial functions include roles such as strategic HR planning, change management, succession planning, organizational development, and policy implementation. On the other hand, operational functions focus on aspects such as recruitment, job analysis, employee retention, and compliance.
Managerial Functions of HRM
Managerial functions of HRM are essential from a policy and management perspective. Some of the key managerial HR functions are HR planning, change management, organizational development, policy formulation, and diversity and inclusion.
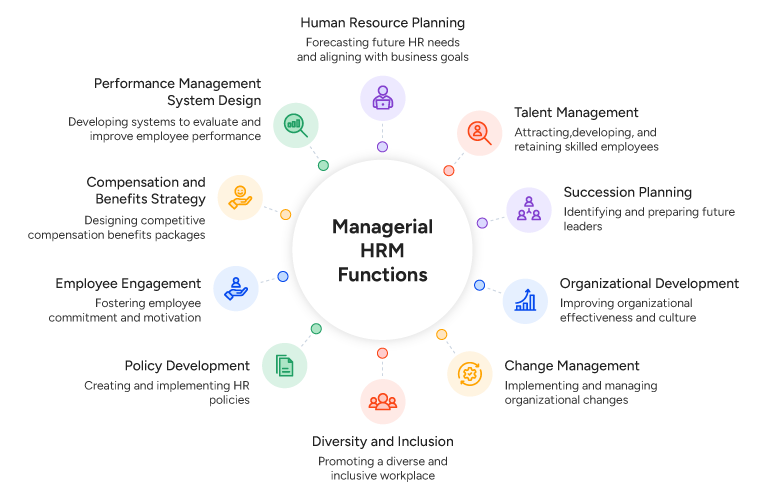
1. Human Resource Planning
Human resource planning is a key HRM function that includes forecasting an organization’s future needs and developing strategies for talent acquisition, employee retention, and talent management. It focuses on analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of the workforce and forecasting future supply and demand. By aligning departmental goals with business objectives, HR planning helps allocate human resources as per organizational needs.
2. Talent Management
Talent management is one of the core HRM functions that includes acquiring and developing talent to meet current and future needs. It encompasses recruitment, onboarding, performance management, and succession planning. Thus, it helps improve performance and develop a leadership pipeline for business continuity.
3. Succession Planning
Succession planning is used by organizations to identify potential employees for future leadership roles. The process focuses on creating a career path for high-performing employees through effective training and development. Succession planning helps retain top talent and ensures a smooth transition in leadership. It is also critical from a risk mitigation perspective.
4. Organizational Development
Organizational Development (OD) is another core HR function that relies on data to identify organizational issues. Being a continuous process, it enables an organization to remain flexible and adapt to changing market conditions. The function is important as it improves change management, work culture, and organizational strategies with data-backed evidence.
5. Change Management
As one of the key functions of HRM, change management manages technological, structural, and other systematic changes. It focuses on clear communication and transparency to improve employee engagement. The function also involves formulating strategies for a smooth transition. Finally, employees are trained to adapt to new technology or other changes.
6. Diversity and Inclusion
This function focuses on creating a work environment that is fair and equal for all employees. It specifically emphasizes equal participation for those sections of society that have been historically underrepresented. Diversity and inclusion are critical HRM functions as they help maintain a diverse workforce with diverse perspectives.
7. Policy Development
Policy development includes creating, implementing, and monitoring policy guidelines. A flexible and well-implemented policy development function helps mitigate risks. It also sets a clear code of conduct, outlining the organization’s values and standards related to expected employee behaviour.
8. Employee Engagement
Employee engagement is a core human resource management function that cultivates positive employee relations through targeted strategies. Firms focus on improving communication and transparency, along with providing more incentives for retaining employees.
9. Compensation and Benefits Strategy
Compensation and benefit strategies are a set of incentives that provide targeted benefits and compensation packages. This is particularly important in attracting new talent and retaining old employees. Organizations typically provide complementary memberships, insurance premiums, and product discounts as benefits. Some companies also reward their employees with performance-based incentives as part of compensation.
10. Performance Management System Design
As a managerial HRM function, performance management system design includes setting goals, reviewing employee performance, and providing feedback. Organizations are increasingly focusing on tools such as 360-degree feedback to provide both internal and external feedback. They also rely on automated systems for measuring KPIs and tracking performance.

Operational Functions of HRM
The operational functions of HRM encompass various activities, including recruitment, job analysis, training and development, and employee and labor relations. Compliance and risk mitigation are also a part of the operational functions of HRM.
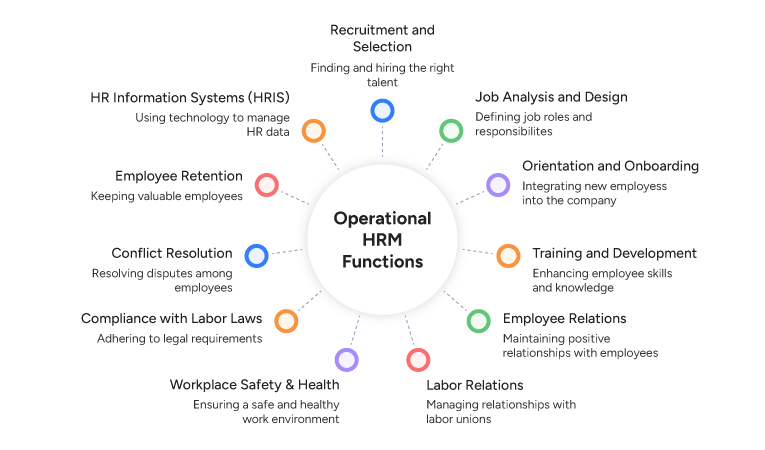
11. Recruitment and Selection
This function focuses on recruiting and selecting candidates who are ideal fits for available job positions. Firms are increasingly focusing on both cultural traits and skill analysis. Leaders rely on HR metrics such as cost per hire and time to hire to improve the recruitment and selection process.
12. Job Analysis and Design
Job analysis involves examining the roles, responsibilities, and skills necessary for a job. Conversely, job design is a process of restructuring a job to make it more appealing to employees. Together, these core functions of HRM help plan recruitment and create tailored job descriptions. Determining compensation is also an important component of job analysis and design.
13. Orientation and Onboarding
Orientation helps new employees understand organizational values and policies. On the other hand, onboarding is a broader function that encompasses training and development, building connections, and role integration. Both of these functions are important as they help employees integrate with the workforce and understand their roles more effectively.
14. Training and Development
This human resource management function helps employees grow by improving performance and productivity. Training and development initiatives also help retain talent and support an employee’s career growth. This function also prepares a workforce for change and aligns employee goals with business goals.
15. Employee Relations
Employee relations is one of the core functions of HRM, focusing on building and maintaining positive employee relations. This function improves employee engagement and satisfaction and fosters a sense of belonging. Some key aspects of this function are conflict resolution, open communication policy, and grievance management.
16. Labor Relations
Labor relations involve negotiating with workers who are part of unions and ensuring compliance with labor regulations. The function helps maintain a productive relationship between management and unions. Leaders implement dispute resolution mechanisms to ensure fair and transparent negotiations. Compliance with labor laws such as the National Labor Relations Law is also an important aspect of the function.
17. Workplace Safety and Health
This function entails creating a safe and healthy work environment for all employees. Professionals develop and implement safety policies, as well as conduct training sessions related to risk mitigation and safety measures. Compliance with regulations such as the Workplace Safety and Health Act and OSH (Occupational Safety and Health) regulations is a critical aspect of this function.
18. Compliance with Labor Laws
In this function, HR professionals ensure that organizational policies and guidelines comply with national and regional labour regulations. In India, it is mandatory for organizations to comply with wage and labor laws, such as the Minimum Wages Act, the Maternity Benefits Act, and the Factories Act, 1947.
19. Conflict Resolution
Conflict resolution addresses workplace disagreements through mediation and policy enforcement. Primarily, this function fosters a harmonious workplace where employees respect one another’s opinions. In serious cases, HR professionals also serve as third-party investigators and conduct investigations.
20. Employee Retention
Employee retention is a core function of HRM that helps organizations retain employees through targeted initiatives. As a part of this function, HR professionals implement targeted strategies and design attractive compensation packages. They also conduct surveys to identify causes of disengagement. Lastly, firms offer remote and hybrid working conditions to improve the work-life balance.
21. HR Information Systems (HRIS)
HR Information System (HRIS) is a system that automates all the key functions of HRM. HR professionals are increasingly utilizing such Human Resources Management Systems for tracking payroll, managing performance, and engaging employees. Leaders also incorporate HRIS into decision-making, as it provides data to guide strategies.
Importance of HRM Functions in 2026
HRM functions are important because they help formulate strategies, manage employee lifecycles, mitigate risks, and provide operational support.
Strategic Importance
HRM aligns employees’ strategies with business goals, shaping workforce planning, leadership, and culture so that human capital drives competitive advantage.
Employee Lifecycle Management
HRM manages the end-to-end employee journey from attraction to exit, optimising recruitment, onboarding, development, and retention to improve engagement and performance.
Risk Mitigation and Compliance
Core functions of HRM related to labor relations, risk mitigation, and compliance with labor laws help reduce risks and comply with the labour regulations of the region.
Operational Support
Operational HR management functions, such as conflict resolution and employee engagement, make the workforce more productive and harmonious.

Conclusion
We covered 21 core functions of HRM that are essential for people management. The managerial functions of HRM are critical from both strategic and management perspectives. These functions include strategy formulation, performance management, succession planning, and organizational development. Operational functions focus on creating a safe, harmonious, and equal environment by focusing on diversity and inclusion and conflict resolution.
Businesses are increasingly adopting solutions that automate HRM functions. For example, firms are leveraging AI-powered features such as predictive analytics for forecasting future needs. Therefore, AI and automation will continue to shape the core functions of HRM in the near future.
Simplify and Automate Your HR Functions with factoHR
FAQ
What is the Difference between Managerial and Operational HRM Functions?
Managerial functions focus on planning, organizing, directing, and controlling HR strategy, while operational functions handle day-to-day tasks like hiring, payroll, and employee relations.
What are the Major Functions of HRM?
Core HRM functions include:
- Recruitment and selection
- Training and development
- Performance management
- Compensation and benefits
- Employee relations and compliance
What is the Role of Human Resource Management in an Organization?
HRM ensures that the right people, policies, and processes are in place to build a productive, engaged, and legally compliant workforce that is aligned with organizational goals.
What Human Resource Management Functions Can be Outsourced to Third-Party Providers?
Commonly outsourced functions include payroll, recruitment, compliance management, benefits administration, and HR analytics.
Why are HRM Functions Important for Business Success?
They improve productivity, enhance employee engagement, ensure compliance, and help organizations attract, retain, and develop top talent.
How are Functions of HRM Evolving with Technology and Automation?
Automation streamlines HR tasks like payroll, attendance, and performance reviews, enabling data-driven decisions and freeing HR to focus on strategic initiatives.
How do HRM Functions Promote Diversity and Inclusion at Work?
HRM promotes inclusion through unbiased hiring practices, equitable pay, diversity training, and transparent performance evaluation frameworks.
Grow your business with factoHR today
Focus on the significant decision-making tasks, transfer all your common repetitive HR tasks to factoHR and see the things falling into their place.

© 2026 Copyright factoHR


