Top 10 DEI Metrics to Track in 2026 for Real Impact

Table of Contents
Have you implemented DEI, and are you confused about which DEI metrics to focus on to measure progress?
In today’s rapidly changing times, organizations are focusing on DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion). Prioritizing DEI fosters a culture of belonging that embraces differences, promotes equal opportunities, and values everyone, benefiting employees and the organization.
Measuring DEI progress is crucial for assessing accountability and identifying areas needing improvement. Evaluating DEI requires a comprehensive strategy and reliable data to provide valuable insights. This data can reveal flaws in the workplace, such as management bias and inequity.
In this article, we provide the top 10 DEI metrics to measure your organization’s progress to help you identify bias in the workplace and work towards a safe, inclusive, and equitable workplace.
What are DEI Metrics?
DEI metrics measure organizations’ diversity, equity, and inclusion. These metrics encompass qualitative data, such as employee sentiment, and quantitative data, like hiring rates. They help determine outcomes and track progress toward goals, identify challenges, and develop strategies for improvement.
DEI must embody a cultural shift that aligns with your organization’s fundamental values and should not be viewed as just a box-ticking activity.

Why are DEI Metrics Important?
DEI metrics provide a measurable way to track progress, identify gaps, and make sure that diversity, equity, and inclusion are integrated into workplace strategies.
Without clear diversity and inclusion metrics, organizations may rely on assumptions rather than implementing effective action.
DEI metrics are important as they accomplish the following:
Accountability: Tracking metrics for DEI progress demonstrates an organization’s commitment and holds decision-makers accountable for results.
Transparency: Transparency is essential in Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI) initiatives. Transparent communication of workforce demographics, hiring practices, pay equity advancements, and promotion statistics shows employees that their employer is committed to an equitable and inclusive workplace.
Identify gaps: DEI metrics offer insights that wouldn’t otherwise be accessible, such as pay disparities, limited opportunities, fewer promotions, and so on. These insights are valuable as they highlight areas that need immediate attention. Subsequently, the Human Resource team can focus on implementing changes to create an equitable workplace.
Substantiates Value: Achieving significant outcomes from DEI programs enables organizations to provide well-founded reasons for valuing diversity and inclusion in business.

How do You Measure Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion?
Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion may vary for different organizations. Measuring it can be complex as these include many variable factors. Other important aspects are social influences and industry trends. Here are a few other factors to consider when measuring DEI:
- Demographic data: Gather demographic data, including age, gender, race, and ethnicity, of your organization’s workforce. This analysis will help you understand your community’s diversity and pinpoint any disparities or areas requiring improvement.
- Inclusion: Organizations can check equity based on demographics by analyzing their turnover rates, promotion rates, and pay equity.
- Equal Opportunities: The organization can guarantee equal opportunities by tracking employee involvement in training sessions and skill development.
- Surveys: Surveys can measure factors like a sense of belonging, fairness, equity, and diversity. Organizations can conduct surveys of employees, customers, or community members to gain insights into their experiences and perceptions of DEI initiatives.
- Policies and practices: Evaluate the current policies and practices to see where DEI is being addressed and where biases or gaps exist. Then, assess your hiring and recruiting practices, promotion, and other criteria to support workplace inclusion.

10 DEI Metrics to Measure Your Organization’s Progress
Implementing DEI alone is insufficient. Organizations may use different KPIs to check DEI progress depending on their specific goals and initiatives. The methods of measurement are just as crucial as evaluating implementation. Determine the metrics that can quantify your organization’s specific DEI objectives.
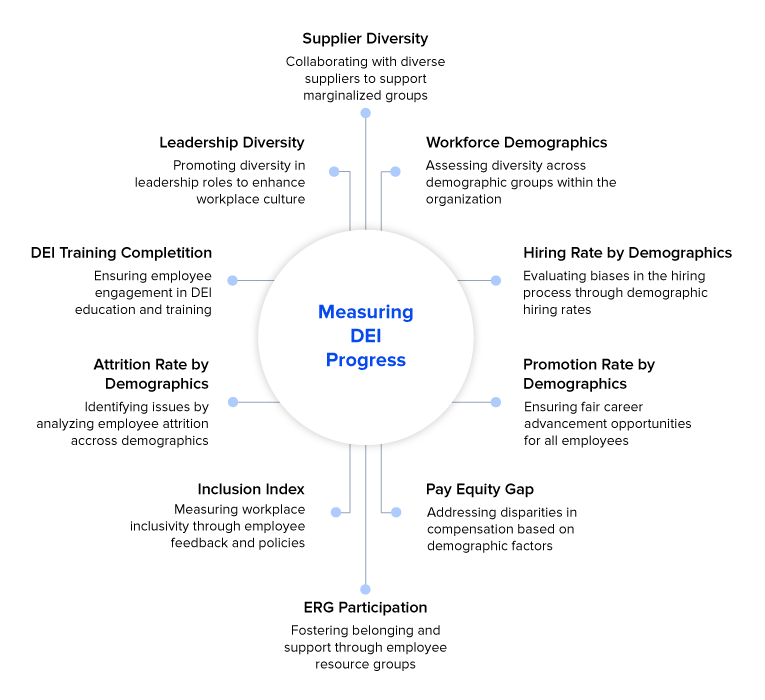
Some of the most important DEI metrics you should consider to measure your organization’s DEI progress are listed below:
1. Workforce Demographics
Workforce demographics are an important metric for assessing diversity within an organization. They indicate the proportion of employees from various demographic groups (like age, gender, and race) at different organizational levels.
This data enables HR teams and business leaders to check for unconscious bias, analyze their workforce across different demographic categories, determine diversity in their organization, and assess the impact of DEI initiatives.
2. Hiring Rate by Demographics
Assess how your organization processes applications, interviews candidates, and recruits individuals from various demographics. The hiring rates of employees from different demographics reveal biases in the hiring process.
Analyzing these rates can highlight inequalities, like a low hiring rate in a specific demography, indicating implicit biases in the hiring process that need to be addressed. Hiring rate is one of the most important metrics for measuring an organization’s diversity, equity, and inclusion.
3. Promotion Rate by Demographics
Fair and equal promotions across the organization are essential for promoting DEI in the workplace. An organization’s promotion rate reflects its dedication to ensuring equitable career advancement opportunities for all employees.
Monitoring the average duration for promoting qualified employees and their promotion rates based on key factors assists in recognizing disparities and guaranteeing fair career advancement opportunities.
4. Pay Equity Gap
Pay equity measures how well employees are compensated for equal work, regardless of demographic factors. Other factors to review the pay equity gap include bonuses, salary hikes, and the leader’s salaries. It is one of the most notable issues of DEI, so it’s important to calculate it regularly.
Addressing pay equity gaps and adhering to HR compliance shows organizations’ dedication to a fair and inclusive work environment.
5. Employee Resource Group (ERG) Participation
ERGs empower your organization and foster a sense of belonging among employees with common identities, interests, or life experiences. These voluntary groups provide support systems for underserved employees, enabling them to engage in sensitive conversations within a safe environment. ERGs offer a platform for employees to connect, share their experiences, and help create an inclusive work culture.
Businesses can track participation levels in ERGs to see how effective they are and gauge their impact.
6. Inclusion Index (Survey-Based)
The Inclusion Index evaluates DEI to provide qualitative and quantitative measures of workplace inclusivity based on employee feedback, demographic data, organizational policies, and HR reporting. It helps organizations to identify their strengths and areas for improvement in promoting an inclusive environment.
Employee surveys and Diversity, equity, and inclusion KPIs, such as demographic representation, engagement and retention rates, and equitable policies, are used to calculate the inclusion index. The inclusion index is important for gaining insights into employees’ experiences, identifying gaps, and driving DEI-based organizational change.
7. Attrition Rate by Demographics
Attrition by demographics refers to losing employees from specific demographic groups. High attrition rates in particular demographics can identify the issues with diversity and inclusion. By examining attrition rates across different demographics, organizations can identify patterns and trends indicating that a specific group may not feel supported or valued within the workplace.
8. Training Completion on DEI Topics
Organizations often use DEI training and education to inform and educate employees about the impacts of diversity and inclusion in the workplace. HR teams should check the participation of employees in the training and development program to determine the number of engaged employees.
DEI should be an ongoing process. DEI training should be integrated with various strategic processes that support a positive DEI culture in an organization.
9. Leadership Diversity
Diversity in leadership can impact your workplace culture and even the profitability of your organization.
Leadership diversity measures the percentage of different employees in leadership positions, such as managers, senior leaders, and executive teams, to help assess equity and experience disparities. Look into your leadership team to see the employees from different demographics, and evaluate the number of employees from various backgrounds who have been promoted to higher positions.
Leadership diversity is important in creating a workplace that focuses on diversity, equity, and inclusion.
10. Supplier Diversity
Diversity and inclusion metrics incorporate not only employees but also the suppliers of an organization. Supplier diversity metrics evaluate the demographics of suppliers to determine the extent to which an organization collaborates with marginalized groups. This indicates that a salesforce supports veterans, women, persons with disabilities, minority-owned businesses, and more.
By monitoring supplier diversity, an organization indicates that it is committed to DEI initiatives beyond internal operations.

Conclusion
Measuring DEI is very important for an inclusive and equitable workforce. However, understanding where to begin and which DEI metrics to track can be challenging. Organizations should identify their goals and select metrics to help them effectively track DEI progress.
With the top 10 metrics mentioned in this article, organizations can ensure accountability, identify gaps, enhance decision-making, and create a more inclusive workplace. This process helps them analyze where they started, assess the impacts, and determine areas for improvement.
Regularly measuring diversity and inclusion metrics is essential for understanding the state of DEI and its progress. It also ensures transparency and stakeholder engagement with the organization.
Grow your business with factoHR today
Focus on the significant decision-making tasks, transfer all your common repetitive HR tasks to factoHR and see the things falling into their place.

© 2026 Copyright factoHR


