Strategic Management: Definition, Importance, Process, and Types

Table of Contents
Strategic management is a process that allows organizations to develop and implement effective strategies for managing their resources. This makes it a critical process in a volatile business environment. By formulating strategies, firms can optimize their resource allocation and outperform their competitors. Additionally, flexible strategies can help adapt to new technological advancements. Strategic management is important for effective leadership and change management.
In this guide, we cover the key aspects related to strategic management, including its definition, purpose, importance, types, and components for implementing the strategic management process. Lastly, we will explore some key trends that are shaping strategies and influencing decision-making.
Quick Summary
What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a continuous process that helps organizations define their long-term direction, allocate resources efficiently, and adapt to change. It combines planning, analysis, and execution to ensure every business decision aligns with the company’s vision and market realities.
Why Is It Important?
In today’s volatile environment, strategic management enables leaders to anticipate risks, make data-driven decisions, and maintain a competitive edge. It strengthens goal alignment across teams, improves resource utilization, and fosters organizational agility.
What Will You Learn in This Guide? This guide explains:
- The definition, purpose, and importance of strategic management.
- The types and components that shape effective strategy execution.
- The key stages in the strategic management process—from goal-setting to evaluation.
- The emerging trends of 2025–26, including agentic AI, predictive analytics, sustainability, and flexible strategy models.
In Short:
Strategic management is not just about planning—it’s about ensuring your organization thrives through clarity, adaptability, and innovation. By understanding how to connect strategy with execution, you’ll be equipped to lead with foresight and achieve sustainable growth.
Connect Strategy with Execution
Streamline your strategic goals and workforce initiatives effortlessly with factoHR’s HR software – designed to simplify planning, automate workflows, and enhance business performance.
What is Strategic Management?
Strategic management is a continuous process of setting goals, analyzing the internal and external environment, and formulating strategies for long-term success.
The concept of strategic management originated in the 1950s with Peter Drucker’s management by objectives. It evolved through contributions from Alfred Chandler, Igor Ansoff, and Michael Porter, who shaped its modern foundations in terms of competition and structure. By 2025, strategic management will be increasingly data-driven and agile.
What is the Purpose of Strategic Management?
The primary purpose of strategic management is to align business activities with the organization’s mission and vision while responding to changing market conditions. Subsequently, there are three main objectives of strategic management, which include:
- Anticipating risks,
- Allocating resources, and
- Maintaining a competitive edge by adapting to new technological advancements.
Importance of Strategic Management
Strategic management is important as it helps align goals, allocate resources, and monitor performance.
- Goal Alignment: Strategic management ensures that everyone – from leadership to frontline employees – works toward common objectives.
- Resource Allocation: It enables efficient use of financial, human, and technological resources by prioritizing the most critical initiatives.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuous evaluation allows organizations to assess outcomes and make adjustments.

Types of Strategic Management
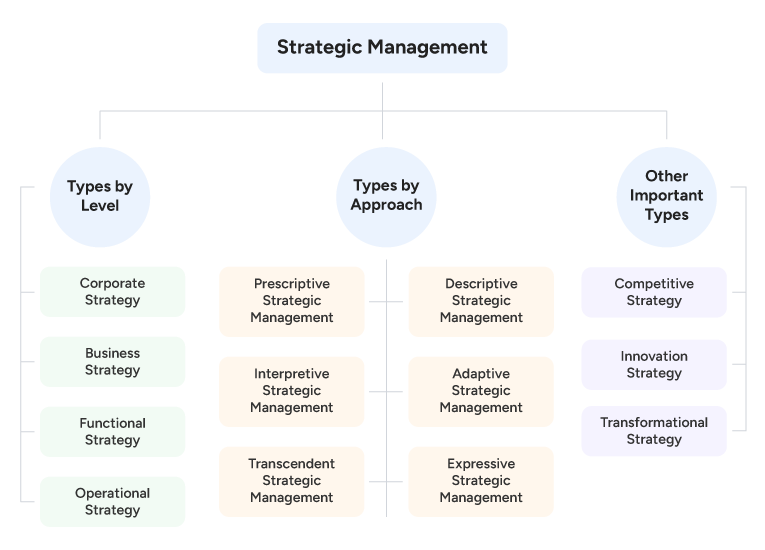
Here, we discuss three types of strategies. These are:
- Types of strategies by level,
- Types of strategies by approach, and
- Other major types of strategies that are not covered in the previous two categories.
Types by Level
This category consists of four types, including:
- Corporate Strategy: Focuses on high-level decisions regarding business diversification, mergers, acquisitions, and long-term growth.
- Business Strategy: Defines how a company competes in specific markets or industries.
- Functional Strategy: Ensures that departments, such as HR, finance, and marketing, align their actions with the business strategy.
- Operational Strategy: Translates plans into day-to-day operations that improve efficiency and execution.
Types by Approach
There are six types of strategic management approaches. These include:
- Prescriptive Strategic Management: Plans are developed before implementation, emphasizing structured decision-making.
- Descriptive Strategic Management: Focuses on how strategies evolve in practice rather than how they should be designed.
- Adaptive Strategic Management: Encourages flexibility to adjust strategies in response to emerging challenges.
- Interpretive Strategic Management: Views strategy as a social process shaped by organizational culture and leadership perception.
- Expressive Strategic Management: Centers on communicating purpose and values to build alignment and motivation.
- Transcendent Strategic Management: Goes beyond conventional boundaries by integrating ethical, social, and environmental perspectives into strategic intent.
Other Important Types
Other important types include:
- Competitive Strategy: Concentrates on achieving a market advantage through differentiation, cost leadership, or focus.
- Transformational Strategy: Involves large-scale organizational change to adapt to major shifts such as digitalization.
- Innovation Strategy: Encourages new products, business models, or processes to drive future growth.
Key Components of Strategic Management
There are four key components of strategic management, including strategic analysis, strategy formulation, implementation, and evaluation.
Strategic Analysis
Strategic analysis involves environmental scanning, SWOT analysis, market assessment, and competitive analysis to understand internal strengths and external opportunities or threats. This step helps organizations identify industry dynamics, assess market potential, and define their competitive position before formulating actionable strategies.
Strategy Formulation
Strategy formulation focuses on strategic planning and goal setting to define corporate strategy and business-level strategy. It establishes clear objectives, allocates resources, and aligns strategic choices with market realities and organizational capabilities.
Strategy Implementation
Strategy implementation emphasizes the execution of strategy through organizational alignment, effective change management, and structured strategy deployment. It converts plans into operational actions, ensuring coordination across departments.
Strategy Evaluation and Control
Strategy evaluation and control ensure continuous performance evaluation using strategic control mechanisms, KPI tracking, and periodic strategy review. This process measures progress against objectives, identifies deviations, and provides insights for timely corrective action, ensuring that strategic goals remain relevant and effectively achieved over time.

What are the Key Steps in the Strategic Management Process?
Strategic management makes it necessary to dedicate to strategic planning. Strategic planning symbolizes an organization’s capability to achieve its short-term and long-term objectives and ascertain the measures that need to be taken to accomplish those goals. Here are the seven stages in the process of strategic management:
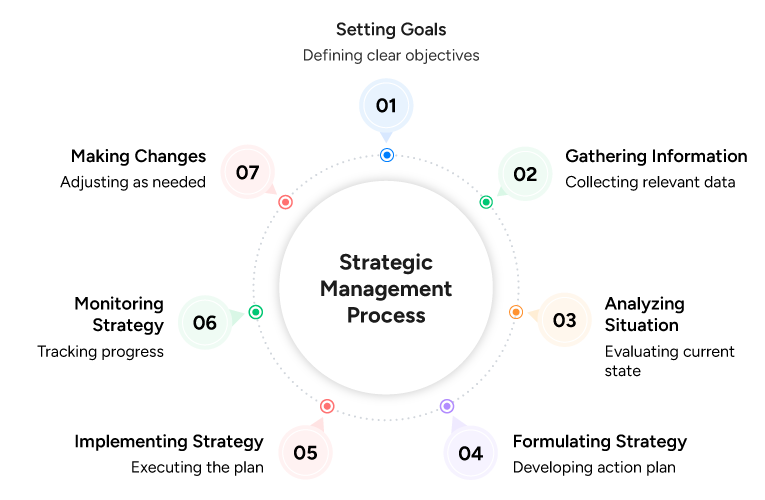
Setting Goals
The first stage of strategic management is to set the goals that the company wants to achieve. This step includes setting up both the long-term and short-term goals. Next, the manager should share these goals with the whole organization and explain how they will impact its future. Each team member gets a sense of purpose for their job and feels engaged.
Gathering Information
The next stage is gathering all the necessary data and information. This information will be an inherent part of the organization’s vision and mission. The information regarding potential future changes, the organization’s market share, competitors’ market share, and other relevant factors are all the questions that need answers.
Analyzing Situation
After gathering the necessary information and defining their vision and mission, the next stage is to assess the present situation. This stage analyses the internal and external environments of the business and assesses its competitors. Finally, managers should categorize all the information based on its relevance to the current situation, considering all the information at hand.
Formulating Strategy
After a thorough study of the information and the situation, the manager must formulate the strategy. The strategy thus made should be clear and transparent. Having a vague plan is worse than having none, as it creates a loss of direction among employees, leading to inefficiency and incomprehensibility.
Implementing Strategy
The best way to determine if the strategy works or not is to implement it. The most critical skills at this level are managerial skills. Communication of the strategy is inevitable, along with an explanation of each employee’s role. The new design must receive support all over the organization to be effectively implemented.
Monitoring Strategy
After implementation, it is essential to monitor the strategy’s success continually. But first, the manager must check if the strategy gives positive results. Then, after testing them out on a smaller scale, the plans should be consistently implemented. This provides stable growth, helps to improve employee retention, and doesn’t affect the organization on a more significant level. Additionally, you can monitor your employees efficiently on a lower level.
Making Changes
If the strategy results in some adverse effects, the manager should reconsider the strategy and make necessary changes. On the other hand, if the process is working fine, the manager can anticipate future problems to create strategies.

What are the Benefits of Strategic Management?
Strategic management can help optimize financial, technological, and human resources. It can also improve the quality of decision-making. Organizations can manage risks and adapt to changes with a well-implemented strategic management process.
Competitive Advantage
Strategic management enables organizations to identify market opportunities and develop capabilities. Through continuous environmental scanning and SWOT analysis, firms strengthen their positioning. This proactive approach makes organizations more sustainable and resilient.
Improved Decision-Making
By integrating structured analysis and strategic planning, leaders make decisions based on evidence. Strategic management provides clarity on trade-offs and priorities. As a result, organizations can navigate challenging times and manage change more effectively.
Resource Optimization
Effective strategic management ensures that financial, human, and technological resources are allocated where they yield the highest value. It eliminates duplication and aligns investments with core objectives. This disciplined approach enhances efficiency and overall returns.
Enhanced Adaptability
In a volatile business environment, strategic management equips organizations to respond quickly to market shifts. Continuous monitoring and evaluation promote agility. Companies that regularly review and evolve their strategies stay relevant and competitive.
Risk Management
Strategic management allows the anticipation, assessment, and mitigation of potential threats through scenario planning and performance reviews. It enables early identification of vulnerabilities. This foresight reduces exposure and strengthens organizational resilience.
Clearer Goals and Direction
Through structured goal setting and alignment, strategic management translates broad visions into actionable objectives. This clarity ensures unified efforts across all business levels.
Increased Productivity
With well-defined strategies, employees understand priorities and performance expectations. Strategic alignment removes inefficiencies and improves employees output quality. The result is a motivated workforce that contributes directly to achieving organizational goals.
Better Collaboration
Strategic management promotes cross-functional alignment by linking individual roles to collective objectives. It creates a shared understanding of purpose and accountability. This fosters stronger teamwork, trust, and interdepartmental cooperation.
Improved Customer Focus
By continuously assessing market needs and customer preferences, strategic management aligns business offerings with evolving expectations. This customer-centric approach builds loyalty and long-term relationships.
Sustainable Growth
Strategic management integrates innovation, risk management, and adaptability into long-term planning. This ensures that growth is consistent and supported by a strong foundation.

Strategic Management: Trends to Watch out in 2026
Here are the top five trends that are influencing market choices from a strategic management perspective:
- Agentic AI: As per Gartner, businesses are increasingly moving towards agentic AI for automating tasks.
- Predictive analytics: Organizations are increasingly relying on predictive analytics for scenario modeling. Firms are also using such capabilities for improving forecast accuracy.
- Sustainability: Firms are prioritizing sustainability measures as a key concern. For example, businesses are focusing on decarbonization and other measures as part of strategic initiatives.
- Flexible strategy models: Organizations are shifting towards flexible strategic management processes, rather than relying on a five-year plan.
- Geopolitics and supply chain resilience: Leaders are considering the fragility of their supply chains due to tectonic shifts in geopolitics.
Conclusion
Strategic management is a necessity. Chief Human Resources Officers (CHROS) will need to implement strategic management processes that are flexible. They will also need to ensure that departments engage in cross-collaboration to meet common objectives. Relying on the various types of strategies, including transformational, business-level, and corporate strategy, can be a good starting point. Consider that strategic management is an evolving process, and knowing the key trends of the time becomes equally important.
Connect Strategy and Execution with factoHR!
Leverage the power of predictive analytics for making informed decisions! Configure policies on the go and communicate them to employees in real-time.
FAQs
When Should Strategic Management be Used?
Strategic management should be used continuously to align goals, monitor performance, and adapt to changing conditions.
What is Strategic Human Resource Management?
Strategic human resource management involves integrating HR policies with the overall business strategy to enhance performance and achieve organizational objectives.
What is the Difference Between Strategic Management and Strategy Management?
Strategic management is a holistic process that spans from planning to evaluation, whereas strategy management focuses on executing and monitoring specific strategies.
What is an Example of Strategic Management?
Apple’s long-term focus on innovation and ecosystem integration is an ideal example of strategic management driving competitive advantage.
What are the Basic Functions of Strategic Management?
The basic functions of strategic management include analysis, formulation, implementation, and evaluation of strategies to achieve sustainable goals.
What are the Key Characteristics of Strategic Management?
The key characteristics of strategic management include a long-term orientation, cross-functional alignment, evidence-based decision-making, explicit trade-offs, continuous monitoring, and adaptability.
Grow your business with factoHR today
Focus on the significant decision-making tasks, transfer all your common repetitive HR tasks to factoHR and see the things falling into their place.

© 2026 Copyright factoHR


