Management by Objectives
Table of Contents
Every organisation, large-scale or small-scale, commercial or non-profit, needs management. To achieve specific goals successfully and efficiently, it is necessary to coordinate and direct the actions of individuals and resources. This blog will look at management objectively in all its elements, traits, and goals. In addition, we will look at several management styles and how they affect organisational performance, such as strategic management, company management, operations management, and product administration.
Management by Objectives or objective of financial management is a comprehensive technique for improving organisational performance. It is a process in which management defines and communicates the organisation's goals to its people to achieve each target.
When concerned about what management is, management strives to achieve specific objectives that are the desired result of each action. They must be received from a fundamental commercial perspective. There are multiple objectives in any organization, and the administration must achieve all of them efficiently and effectively. Organisational aims, social objectives, and personal or individual objectives are all possible categories.

What is Management by Objectives (MBO)?
Let’s first answer what the objectives of management are. MBO (Management by Objectives) identifies and uses key company goals to set personal objectives. MBO methods define an employee's primary objectives, which are then rated using group input.
This allows all corporate contributors to view their accomplishments concerning the firm's critical priorities as they complete their tasks. It emphasises the link between activity and outcome, which significantly boosts productivity.
Though MBO seeks to assist in defining and managing a set of objectives, each company's objectives will differ slightly. It enables businesses to showcase their uniqueness and top goals while executing them more significantly.
How Does Management by Objectives Work?
MBO is a full-scale organisational approach involving individuals from the top to the bottom of the production chain. At the start, the managers determine the company's major aims. Next, they devise ways to communicate firm goals to employees.
The single notion driving this management paradigm is clarity. Employees perform better when they understand their goals, which are challenging but also attainable. You can follow some guidelines to avoid any management mistakes.
All objectives are quantified and tracked to ensure that the tactics are effective. Finally, the personnel receive comments on their performance. Over time, the organisations refine their goals and boost overall output.
Types of Management Objectives
Organisational Objectives
The management is responsible for setting and achieving the company's objectives. It must meet various objectives in all activities while considering the interests of all owners, including stakeholders, consumers, the government, and employees. The primary goal of any corporation must be to maximise the potential advantage of its material and human resources, i.e., to achieve its financial objectives.
Social Objectives
They include creating benefits for the community. Every business, whether trading or non-trading, has a social obligation to fulfil as a member of the community. This refers to continually creating financial value for many aspects of society. This involves adopting environmentally friendly production processes, creating work opportunities for underprivileged members of the community, and providing staff with basic amenities.
Individual Objectives
Organisations consist of people with diverse backgrounds, work experiences, goals, and personalities. They all join the establishment to suit their various demands. These are distinct from economic necessities such as generous perks and compensation, social obligations such as equal attention, and higher-level demands such as personal growth and progress.

Critical Elements of Management Objectives
Focusing on Business Goals
The primary goal of MBO is to identify individual goals and connect them to more significant organisational goals. This allows organisations to strike a balance between their long-term goals and the needs of their employees.
Important Areas for Results
MBO focuses on improving performance in critical areas of the organisation. Identifying KRAs ensures that prioritised areas receive the necessary attention and significantly impact the organisation's performance and growth.
Multiple Liability
MBO ensures that responsibility for a specific target is spread across multiple departments rather than under a single leader. This helps to develop a decentralised planning system with centralised control and responsibility, thereby conquering 'credit grabbing' and 'staff fatigue' issues.
Clarity and Flexibility
MBO is widely applicable and can be used by organisations of all sizes, regardless of industry, market conditions, geographical location, or leadership style. As a result, it is a non-specialist approach used by both small and large organisations.
Comprehensive
MBO is a comprehensive approach that combines financial and human factors, micro-level analysis, and macro-level planning. This enables businesses to manage both long-term and short-term objectives effectively.

What are the Objectives of MBO?
Optimise Resources
Management teams strive to maximise resource utilisation to achieve the highest possible output. This goal allows for increased earnings by reducing the ratio of resource costs to profits. Management teams employ logistical techniques and procedures to identify and eliminate inefficient and resource-intensive activities.
Encourage Individual Growth
An effective management team prioritises the growth and development of its employees. Seminars, mentorship programmes, training tools, and internal promotions allow employees to learn new skills and advance their careers. Employee personal development and progress can also contribute to the growth, quality, and efficiency of work produced, assisting management in meeting financial management objectives.
Maintain Consistency
Management teams are in charge of the rules, procedures, and parameters that govern the production and distribution of goods and services. Maintaining the organisation's quality standards is a primary management goal. The team collaborates with other departments, managers, and employees to create, implement, and sustain quality. According to Forbes, there was a 21% profit increase for all organisations that have a highly engaged work culture.
Increase Efficiency
Improving operations, production, and service efficiency increases output, sales, and profits. Management systems track workplace procedures, duration, and flow to determine which methods produce the most efficient results. Managers may work with employees and department leaders to create and implement new processes and requirements.
Maintain Workplace Morale
An organisation's culture, attitudes, and morale can all impact overall productivity and revenue. Employee morale improves, motivating them to complete tasks and put forth more effort. Management teams strive to maintain morale by establishing effective authority structures, creating incentive programs, and listening to employee feedback. Valuing people and maintaining positive relationships boosts morale and encourages them to grow.
Minimise Risk
Many managerial professions rely on forecasting and projecting results and changes. One of the primary goals of managers is to reduce the likelihood of risks and losses through planning and forecasting. Reducing risk factors such as safety concerns, wasting resources, and unnecessary spending can help increase profits while decreasing losses.
Increase Profits
Management teams strive to balance increasing revenue and creating a positive work environment for their employees. Usually, the finance department is responsible for analysing profits. Profit maximisation requires collaboration with various departments and leaders, such as accountants, supervisors, and executives, to identify opportunities for growth and change. Managers can increase profits by eliminating unnecessary expenses and waste and creating new procedures for more efficient operations.
Develop Business Strategies
Management teams frequently use higher-level critical thinking and abstract strategy to improve operations and revenue. The team collaborates with executives, leaders, and stakeholders to create, present, and implement comprehensive business strategies and frameworks. Creating an effective and consistent corporate plan can help identify and narrow objectives so all employees can work towards a common goal.
Talent Recognition
An organisation's management strives to find, acquire, and retain exceptional candidates and personnel. Managers can work with recruiters to define hiring requirements, evaluate candidates, and make recruitment offers. Identifying and hiring talented and competent employees boosts an organisation's overall knowledge, competence, and productivity.
Workflow Synchronisation
An organisation's workflow and internal structure can influence its productivity and efficiency. Management teams may work with logistics, engineering, and production experts to design logical and efficient workflows, internal structures, and facility layouts. Managers can use organisation charts, flow diagrams, and procedure audits to examine and describe workflow processes.
Ensure Availability
Management teams coordinate, maintain, and forecast the availability of resources, goods, and services. To accomplish this goal, managers can forecast and anticipate the needs of the organisation or the general public and monitor situations such as shortages. Predicting and addressing issues allows the management team to plan and implement changes to prevent production and distribution delays.

Advantages of MBO Management
Personalisation of Objectives
Employees are assigned activities that match their skill sets and best utilise their abilities rather than having to focus on a slew of jobs that they may not be as knowledgeable about.
Efficiency
The highly organised character of MBO, along with the obligation to quantify time-bound objectives, tends to lead to higher levels of production and efficiency.
Defined Boundaries
The amount to which financial management's objective is articulated among management and subordinates establishes clear expectations and boundaries for employees to meet.
Improved Communication
MBO demands comprehensive discussions between company employees at all levels to function properly. As a result, communication between employees, between employees and management, and between managers improves and strengthens.
Self-Direction
Because MBO requires employees to set personal and individual goals to achieve the larger business goals, employees are more self-directed in their daily operations.
Transparency
An MBO demands a breakdown of all aspects and tasks required to attain a goal. Furthermore, it requires businesses to be completely open about their key goals with their personnel.
Increased Engagement and Accountability
MBO's structure, communication, and transparency serve to strengthen employee engagement by providing a clear understanding of their position. Furthermore, the personalised nature of individual objectives results in increased degrees of accountability.

Disadvantages of MBO Management
Inhibits Growth
Because employees keep within their well-defined lanes of responsibilities and production, they have little potential to advance beyond their comfort zones.
Weak Infrastructure
Concentrating on broad aims and business goals can lead to disregarding firm infrastructure and routine activities. This can lead to blunders and mistakes by personnel unaware of how to fix difficulties within the company's infrastructure.
Slow to Set-Up
The overall MBO system can make achieving objectives more efficient. However, the process of establishing and agreeing on all the set objectives can become quite lengthy. If management cannot decide upon the most important goals, it can lead to cancelling out the efficiency above.
Negative Competition
The appraisal and reward system has the potential to create tension among employees. This tension can develop into negative competition, in which employees become less cooperative and communicative with one another to outperform one another.
Employees who define their own goals may become too narrow-minded and unable to try out creative or inventive solutions when issues arise, significantly if those answers deviate from the established rules and restrictions.
No Room for Errors
Managers may begin to require excessive precision and perfection from staff, making minor faults or mistakes appear much more severe.
Not Enough Emphasis on Conclusions
The MBO phases may emphasise setting objectives rather than developing and executing strategies for achieving those objectives.

Tips to Ensure MBO Implementation
Identify the Beginning Point
You must first identify the starting point if your goal is to increase, improve, or develop functions or results. Examining current data or methods establishes a baseline and allows you to set realistic goals for improvement.
Track Your Progress
Setting a target is merely the first step. After establishing your goal, create a plan and metrics for measuring and tracking the changes and progress.
Revise Goals
By revisiting and amending earlier objectives, you may guarantee they stay relevant and achievable as changes, issues, and capacities evolve. Keeping management objectives linked with the organisation's capabilities and rules ensures the message is clear and constant.
Communicate Information Properly
Management objectives go beyond the participants of a management system. Communicating goals, plans, and progress to employees and executives helps ensure every team and person works towards the same goal and sets uniform expectations for employees and management.
Respond to Feedback
Many management objectives seek to improve working conditions and operations for employees and customers. Listening to and responding to input on procedures, policies, and customer satisfaction can aid in developing objectives for improving experiences.

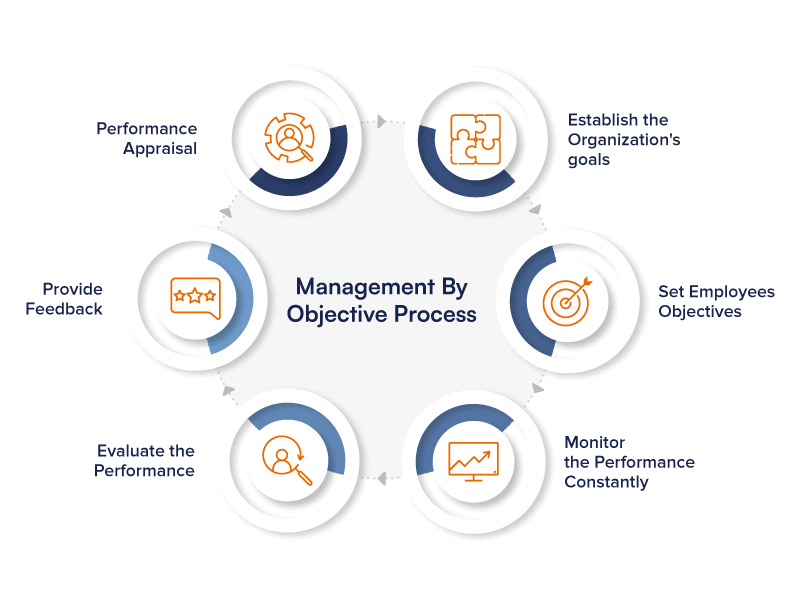
Steps for the MBO Process
Define Organisational Goals
Setting goals is important for a company's development and serves a range of other functions. Setting goals requires the participation of various managers. The supervisors' objectives are temporary, based on an interpretation and judgement of what the organisation can and should achieve within a given timeframe.
Define Employee Objectives
Once employees have been briefed on the overall objectives, strategy, and techniques, supervisors can begin working with their subordinates to set personal objectives. This will be a one-on-one meeting in which subordinates will inform supervisors about their targets, which goals they can achieve within a specified timeframe, and with what resources. They can then give preliminary ideas on goals the organisation or department can consider attainable.
Continuously Monitor Performance and Progress
Though the management by objectives strategy has significance for enhancing manager effectiveness, it is also critical for analysing each employee's performance and advancement within the organisation.
Performance Evaluation
Within the MBO framework, the performance evaluation is carried out with the participation of the managers involved.
Provide Feedback
In the management by-objectives strategy, the most crucial stage is continual feedback on results and objectives, which allows employees to track and modify their activities. Managers can also ensure how they can make the performance feedback effective. Providing continuing feedback is supplemented by frequent formal evaluations that are done during the meetings. Usually, the superiors and subordinates can discuss the progress towards achieving the goals, which leads to additional feedback.
Performance Appraisal
Performance reviews are routine assessments of employees' success within MBO organisations.
Conclusion
Though the objective of financial management is outdated, it can be a helpful starting point and tool within a more extensive toolkit for many businesses trying to enhance their management style. Management by Objectives focuses on establishing objectives and preparing personnel for high productivity and success. Management teams should be aware of being too narrow-minded when adopting MBO and remain sensitive to potential difficulties.
The MBO strategy is used to ensure that employees have a clear grasp of their roles, duties, and expectations so that they may comprehend how their activities contribute to the organisation's overall success. If you want to review your objective of the management model, you can implement actions for it.
If organisations do not appropriately develop, decide on, and control the management by objectives strategy, self-centred personnel are more prone to misinterpret results, portraying short-term, narrow-minded aims as achieved.

People also search for
FAQs
Why is it necessary to have objectives?
Setting an objective provides context for actions and decisions. When a team works together, having a common clear goal allows everyone to understand and contribute to the same outcome. Decision-making and problem-solving procedures require an objective to determine the best techniques and alternatives for achieving the goal while adhering to rules and regulations.
Who was the first to mention objective-based management?
Peter Drucker coined the term 'management by objective' in 1954 in a book called The Practice of Management. The strategy gained popularity in the 1960s and peaked in the 1980s and 1990s when setting annual staff objectives became the norm.
What is the objective of marketing management?
The objective of marketing means the results that any company wishes to achieve through its marketing operations to promote its brand. It should be set so that you may plan all your efforts strategically and effectively to achieve it.
Why is it essential to implement MBO in an organisation?
MBO is essential because it can meet organisational and departmental goals, increase staff commitment, and improve productivity.
What is the degree of management?
Management levels are the distinctions between levels of authority and responsibility in a corporation. There are three traditional management levels: top-level management, mid-level management, and first-line management. These levels define the responsibilities of various management positions, such as who they report to and who reports to them.
What are the concepts that fall under management?
Management theories are a set of ideas that provide guidelines for all organisations and businesses in their daily operations. They discuss how managers use these concepts to achieve organisational goals and motivate employees to perform to their full potential.
What are the objectives of financial management?
Financial management aims to maximise profits. It provides information about increased raw material costs, which may increase the cost of the products sold indirectly. Tracking liquidity and cash flows Ensures that the company has enough funds on hand to pay all debts.
Modify your HR and payroll tasks with factoHR today
Let your HR and workforce focus on most important business decisions while factoHR can reduce the burden of daily activities of the organization.

© 2026 Copyright factoHR


